In deciding what to do next, in terms of customer master data management, it is important to understand what your organization does with its master data and how it manages it.
I say, do next, because there has to be an implicit assumption that whatever you’re doing today, there is a good chance that you want to do what you do even better!
Establishing a good understanding requires an assessment of the “maturity” of the master data management function in your organization.
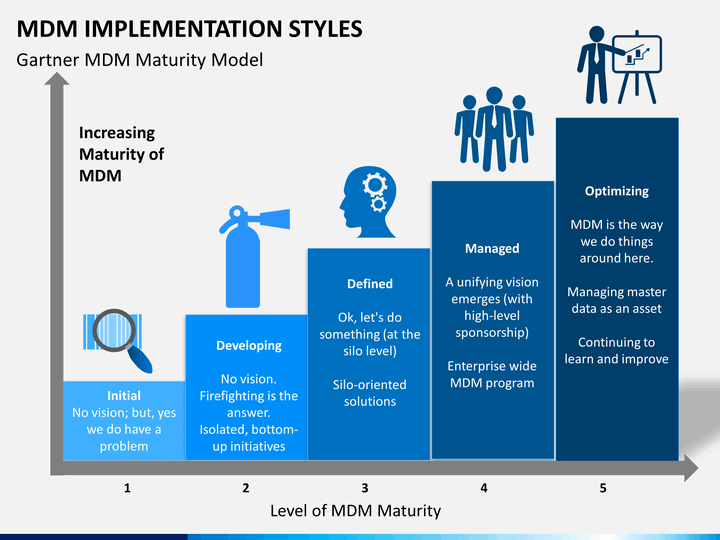
It’s suggested that using a Capability Maturity Model (CMM) is a good way of determining the degree of formality and optimization of existing operational processes. This includes identifying ad hoc practices and formally defined steps in the end-to-end process.
The end result may also be Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), managed result metrics (OKR measures) and active evolutionary optimization of the data mastery practice over time.
The CMM is based on a development model created in the 1980s for the U.S. Department of Defense which funded a study of data collected from organizations that contracted with the DoD.
The MDM maturity model, a derivation of the CMM, is a means of assessing the whole process of master data management including the data point of view and also focusing on the whole operational process.
No need to boil the ocean
Investopedia Definition
A common misconception is that master information consolidation is always “the best approach to master data management”. The reality is that different parts of the business have different needs and expectations around master data and around the customer master in particular. The idea that you need to “boil” the proverbial ocean of data that you have, to reduce your data to the essential most valuable nuggets that your business requires, assumes that you know the requirements of the business.
The stark reality is that even if you do manage to converge on a single source of truth for the whole organization, the way the different stakeholders curate, manage, maintain, use and disseminate the customer master, may well be wholly incompatible with the governance choices that you make.
No one will deny the fact that operational inefficiency, unreliable operations reporting, customer dissatisfaction and regulatory compliance issues often have roots in inadequate data management.
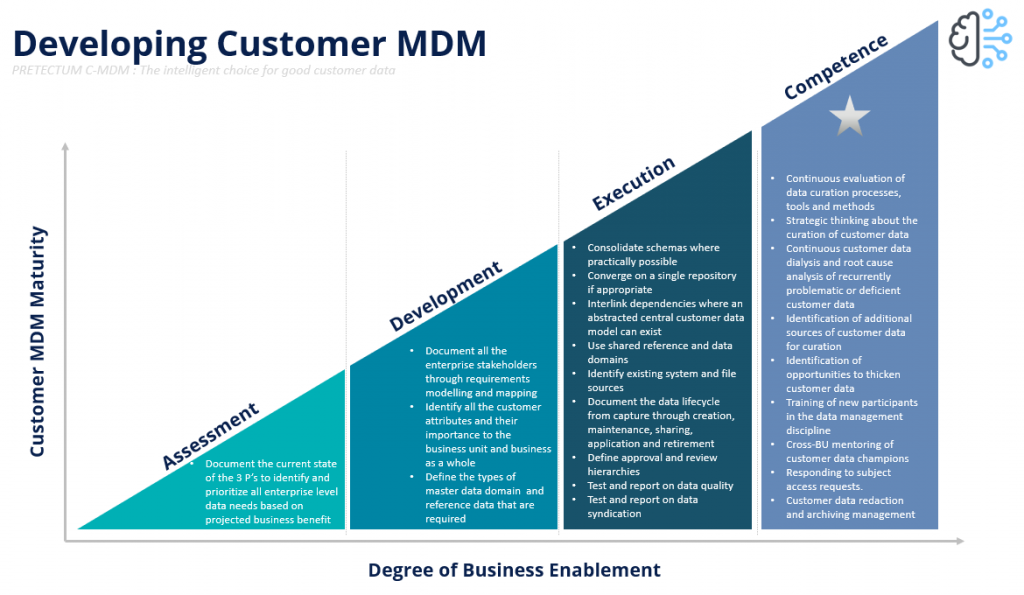
Further, the implementation of advanced analytics and reporting and an increased level of interest in the “digital everything” is forcing organizations to rework their data management model. Taking stock, then of what you do today is important in deciding what decisions you should take strategically and tactically to improve data management operations.
One opportunity lies in the Gartner MDM maturity model. This proprietary model is positioned to give data and analytics leaders a framework to measure and assess their organization’s MDM capabilities, create an MDM vision, and establish a roadmap to reach it.
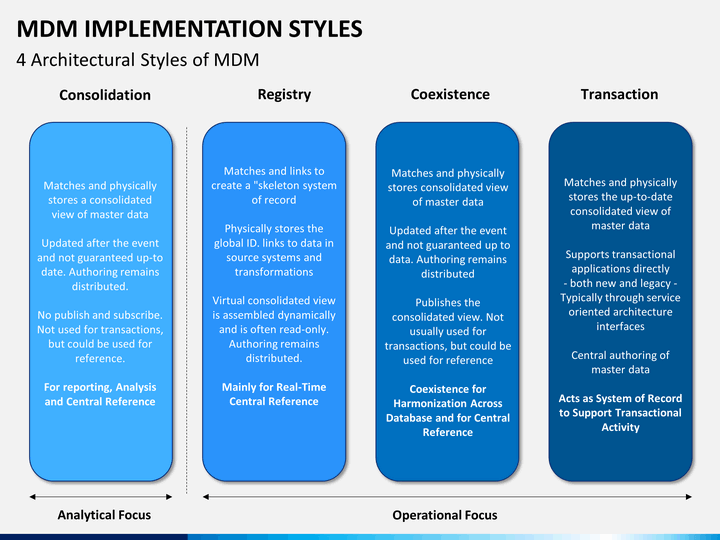
Master Data can be stored in several ways and implemented in a range of styles. It is considered that there are at least four popular master data management (MDM) implementation styles, and their different characteristics suit different organizational needs. Gartner popularises these four and again, it is important to understand, in the evaluation of your own organization’s data mastery setup, which of these is most aligned with the way your business operates.
Consolidation
Support for business intelligence (BI) or data warehousing (DW) initiatives. Often considered as a downstream MDM style. MDM is applied downstream of the operating systems where master data is originally created.
Registry
An index to master data that is authored in a distributed fashion and remains fragmented across distributed systems.
Coexistence
Master data authoring is distributed, but a “golden copy” is maintained centrally in a hub. The central system publishes the golden copy of master data to subscribing systems.
Centralized
When master data is authored, stored, and accessed from one or more MDM hubs, either in a workflow or transaction-based use cases.
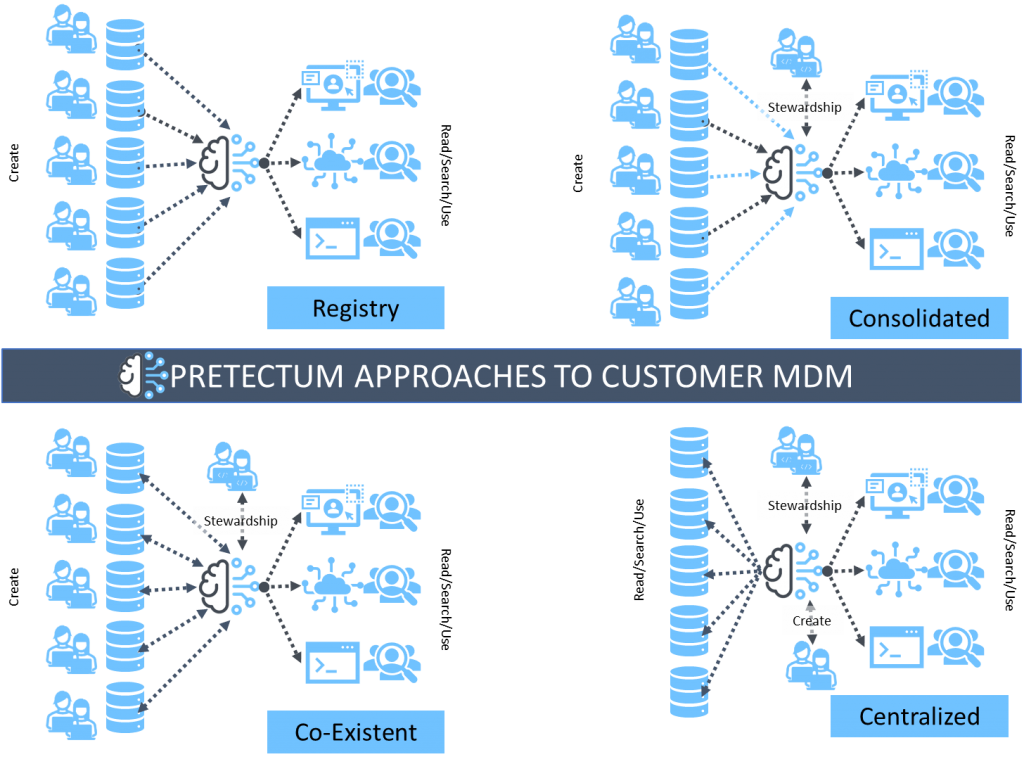
In your self-assessment consider how mature your master data management is and which of these styles is most aligned with the way you work.
When you consider a solution like the Pretectum CMDM, we’re offering support for all stages of the maturity model and all styles of MDM deployment for the customer master. How you choose to do it is at your discretion.
We have best practices but in the end, the best practice may not be the best practice for your business!