According to Statista, 2023 saw an extraordinary spike in data breaches in the US alone.
“As internet usage continues to increase, so does the amount of personal information and data that is made available online. This could be out of choice, for example, somebody providing personal details to a social network in order to use their service – or it could be unwillingly, as a victim of a cybercrime attack or data breach. With the development of various AI tools, cyber crime is currently transforming. Therefore, the risks to individuals, companies, organizations, and governments have never been greater.“
Ransomware
Share of organizations that pay ransoms after a ransomware attack
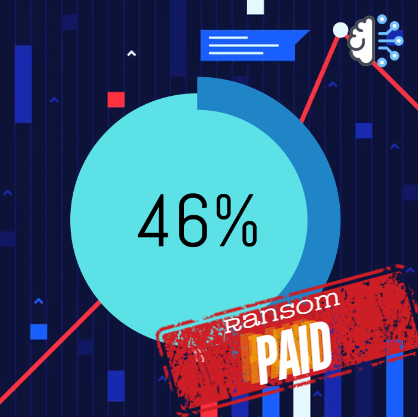
In 2023, customer data breaches exhibited several common characteristics that highlight the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
Increase in Data Breaches
There was a 20% increase in data breaches from 2022 to 2023, with over 5 billion records compromised by October 2023 alone. This surge indicates a troubling trend in the frequency and scale of such incidents.
Some of the main causes are cloud infrastructure misconfiguration, with a significant portion of breaches (over 80%) involving data stored in the cloud, often due to misconfigurations that expose sensitive information. Ransomware has become increasingly prevalent, accounting for approximately 24% of all malicious cyberattacks.
Ransomware intensified, with a 50% year-on-year increase during the first half of 2023. The average ransom payment skyrocketed from $400,000 to $2 million, indicating that these attacks are becoming not only more frequent but also more financially burdensome.
The sophistication and organization of these attacks have also escalated, with ransomware gang activity rising significantly, particularly in regions like the Middle East. There was also the exploitation of Vendor Systems with attackers frequently targeting third-party vendors to gain access to larger networks, reflecting a shift towards exploiting interconnected systems rather than direct attacks on primary targets.

Cybercrime Worldwide
Cyber criminals becoming more sophisticated in their tactics. Projections for 2024 are 9.22 trillion dollars and 13.8 by 2028 in cybercrime alone.
The most common initial attack vectors were phishing schemes and the use of stolen or compromised credentials, which facilitated unauthorized access to sensitive systems. Such phishing attacks saw a dramatic increase, with billions of malicious emails sent daily. There were also a number of application-layer Attacks, these surged by as much as 80%, indicating a growing vulnerability in web applications that are critical for business operations.
The financial consequences of data breaches are significant, with the average cost per breach reaching around US$4.5 million in 2023, reflecting a 15% increase over previous years. There is an urgent need for organizations to enhance their cybersecurity measures accordingly.
The finance sector was the most breached industry, it accounted for some 27% of all breaches reported by Kroll, a notable increase from 19% in 2022. Such a rise is attributed to various factors, including the exploitation of vulnerabilities by ransomware groups like the CLOP ransomware gang, which targeted regional banks and third-party vendors.
Customer Data and Data Breaches
Consumer customer data is a strong target for data theft, primarily due to its high value and the sensitive nature of the information it contains. Customer data often includes personal identifiable information (PII) such as names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and financial details like credit card information and banking credentials.
This type of information is invaluable for identity theft and fraud, making it a prime target for hackers looking to exploit individuals or organizations for financial gain.
The frequency of data breaches having surged, with an 8% increase in global weekly cyber attacks reported in 2023. Many organizations remain underprepared to defend against these threats, which allows attackers to successfully infiltrate systems and access sensitive customer data .
Not only do external hackers pose a risk, but insider threats are also significant.
According to this Intel Security report, Grand Theft Data II: The Drivers and
Shifting State of Data Breaches – internal actors may be responsible for as much as 43% of data loss, half of which is intentional, and half accidental. Customer and employee information were the top two content categories, according to the report. Employees or contractors with authorized access can exploit their privileges to steal customer data.
Given the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, the high value of customer information, and the potential for significant financial losses, consumer customer data remains a prime target for data theft. Organizations must prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to protect this sensitive information from both external and internal threats.
What can you do?
To mitigate future data breaches, organizations can adopt a comprehensive approach that significantly enhances their cybersecurity posture.
This involves strengthening identity and access management through the implementation of multi-factor authentication and adhering to the principle of least privilege, ensuring users have only the access necessary for their roles.
Enhancing incident response and recovery plans is crucial, as organizations should develop and regularly update these plans while conducting cyber recovery exercises to improve readiness. Establishing comprehensive security policies that encompass access management, employee training, and compliance with regulations is essential, alongside robust logging and monitoring systems to detect unusual activities in real time.
Regular security audits and assessments, including vulnerability scans and third-party risk evaluations, help identify and remediate weaknesses.
Investing in employee training and awareness programs is vital to educate staff about cybersecurity threats like phishing and social engineering, fostering a culture where reporting suspicious activities is encouraged. Utilizing advanced security technologies such as data loss prevention solutions and threat intelligence tools can provide proactive defenses against emerging threats.
Additionally, securing network infrastructure through segmentation and strict patch management helps limit potential breaches. Finally, engaging with law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity resources can provide valuable assistance during incidents, ultimately enhancing an organization’s ability to protect sensitive information and maintain trust in its services.
Which of these have you adopted?
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials. |
| Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) | Ensure that users have the minimum level of access necessary to perform their roles, which limits potential damage from compromised accounts. |
| Incident Response Plans (IRP) | Develop and regularly update incident response plans that include clear communication protocols and post-attack workflows. |
| Regular Drills | Conduct regular cyber recovery exercises and simulations to test the effectiveness of incident response strategies and improve readiness. |
| Enterprise-wide Security Policy | Establish a security policy that covers access management, employee training, and compliance with regulatory requirements. |
| Logging and Monitoring | Implement robust logging and monitoring systems to detect unusual activities promptly and respond to incidents in real time. |
| Vulnerability Scans | Perform regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and remediate security weaknesses in systems and applications. |
| Third-Party Risk Management | Continuously monitor and evaluate third-party vendors for security risks, ensuring they comply with your security standards. |
| Security Awareness Programs | Provide ongoing training for employees about cybersecurity threats, including phishing and social engineering tactics, to reduce human error risks. |
| Encourage Reporting | Foster a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities or potential security incidents. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Deploy DLP solutions to monitor and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or exfiltration, particularly from insider threats. |
| Threat Intelligence | Implement threat intelligence tools to gain insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities, allowing for proactive defense measures. |
| Network Segmentation | Segment critical network components to limit lateral movement within the network in the event of a breach. |
| Patch Management | Maintain a strict patch management schedule to ensure all systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches |
Pretectum’s role in protecting customer data assets
Pretectum CMDM (Customer Master Data Management) offers a comprehensive solution for businesses looking to enhance their customer relationships, customer data management and customer retention.
Single Customer View
Pretectum CMDM integrates customer data from any and all your customer data systems, it then provides a holistic view of the customer profiles. This integration enables businesses to make decisions based on data by analyzing the data centrally despite the multiple touchpoints. Depending on your configuration, the systems can house customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing pattern indicators. This in turn allows for tailored products and services that might meet specific customer needs.
Working with Live data
Through the combination of integration, direct data entry, and data syndication, the platform supports the use of advanced analytics and makes use of real-time data processing and data evaluation to enable any organization to quickly adapt their thinking in response to evolving perspectives on customers and markets, through the examination of customer profile data. This agility is important for maintaining competitiveness in today’s fast-paced environment.
Centralized proactivity
By employing a combination of structured and unstructured data modeling the platform helps support the identification of customers with particular characteristics. This capability supports the implementation of proactive measures, allowing businesses to engage customers through appropriate personalized communication and engagement.
By centralizing the customer data profiles, it becomes possible for the various departments such as marketing, sales, and customer service to work cohesively from the same customer data. This fosters collaboration and ensures a unified approach to customer engagement and management, enhancing the overall customer experience.
The system collates extensive customer data profiles, which enables the potential for identifying untapped opportunities for innovation, products, services, and engagement. By leveraging centralized customer data effectively, organizations can exceed customer expectations and solidify their market position..
Addressing risks and privacy
While offering numerous organizational benefits in terms of data management in general, Pretectum CMDM also provides important capabilities in support of data usage and data privacy concerns. These include features for self-service data verification and consent management, ensuring that businesses can manage customer data responsibly while enhancing trust. Smart contracts automate this process, ensuring that consent is recorded and maintained without the need for complex legal agreements. This not only simplifies compliance but also enhances user experience by reducing friction engagement.
Pretectum’s blockchain creates an immutable ledger where every transaction related to the customer data is recorded. Once data is entered into the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring that the history of changes is preserved and verifiable. This feature is crucial for maintaining data integrity and trust, as it provides a reliable record of all modifications made to customer information.
With Pretectum’s blockchain, there is greater traceability of the customer data. Each change in the customer master data is timestamped and linked to previous entries, creating a chronological chain of events. This transparency allows businesses to track how customer data has evolved over time and ensures compliance with compliancy regulations and provides clear audit trails.
The cryptographic nature of Pretectum’s blockchain enhances the overall security of the customer data it stores. By encrypting sensitive information and making it accessible only to authorized parties, the blockchain in turn reduces the risk of unauthorized access and potential breaches. This security layer is vital for protecting customer data integrity and privacy.
Contact us to learn more


