Per a definition from industry analysts and consulting group, Gartner, “Application data management (ADM) is a technology-enabled business discipline in which business and IT work together to ensure uniformity, accuracy, stewardship, governance, semantic consistency and accountability for data in a business application or suite, such as ERP, custom-made or core banking.” For most organizations, ADM encompasses the management of Customer Master Data and other related information as used by the applications in operation.
In the Pretectum CMDM context, this is typically the actual Customer Master Data in CRM, ERP, POS, or a webshop, and may include other information that would be used by applications such as reference data for picklists or validation (Pretectum Business Area Data).
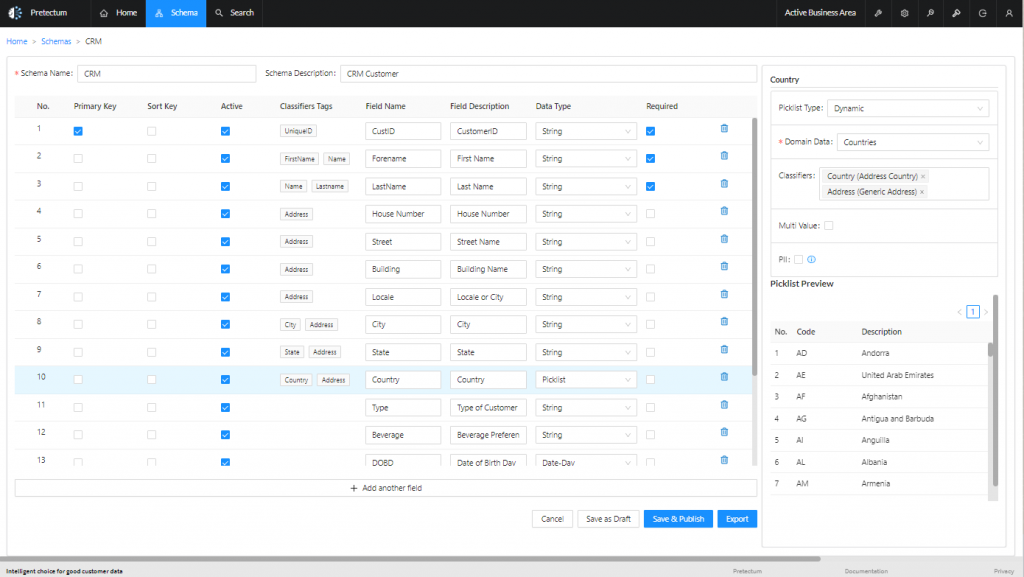
In the absence of continuous integration, the data structures (Schemas) and business rules (Schema column or field validation settings) may be manually configured in the Pretectum CMDM platform to conform in parallel to those of the application itself.
Manual configuration facilitates several key functions:
- Bulk Data Management: Pretectum supports the bulk import of datasets, allowing for either dataset appends or overwrites as necessary.
- Record Editing: Pretectum enables individual record editing within the platform, facilitating the modification or addition of records about customers.
All of these data management processes adhere to the strictly (or loosely) defined schemas and rules associated with each data attribute within the Pretectum CMDM platform, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
By implementing ADM practices within Pretectum CMDM, an organization can streamline data management processes, enhance data quality, and ensure compliance with established business rules and standards.