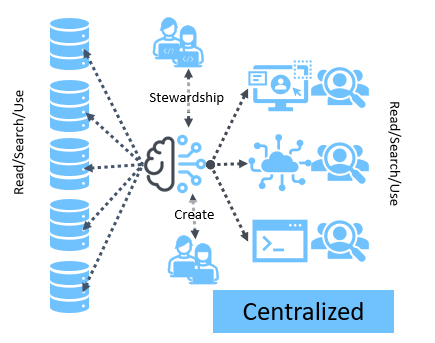
The evolution of Master Data Management (MDM) and customer MDM (CMDM) in particular, has brought to light the significance of centralized data security, access controls, and metadata interoperability.
Enterprises often grapple with data management issues arising from the decentralized nature of their applications and systems. Stovepipe applications, with their isolated data silos and inconsistent access controls, can create a labyrinthine of complexities. The challenge becomes more pronounced when determining who can access or modify specific data and exercise authorized actions.
The need for centralized enterprise data access controls becomes obvious as a requirement in order to mitigate these issues. A dedicated enterprise data security and visibility system can efficiently manage and enforce data access permissions, eliminating redundancies that stem from multiple applications trying to govern the same aspect of data access. This not only streamlines customer master data governance but also enhances security and compliance efforts, as it becomes easier to manage and audit data access to customer records across the entire organization.
As the technology landscape continues to expand, the integration of various systems and technologies becomes imperative. Customer MDM technologies are no exception to this trend. They need to seamlessly interact with external authorities for authentication and authorization purposes. This integration enables the CMDM system to leverage the existing authorization, eligibility, and security rules of external systems, ensuring a cohesive approach to data security.
An open CMDM product seamlessly exchanges data with a central enterprise-wide data security and visibility product and transforms data security practices. Such an approach not only bolsters the overall quality and resilience of data security and visibility solutions but also contributes to cost reduction. When you decouple data security and access controls from individual applications, the organizations achieve better consistency and control all the while minimizing duplication of effort.
Data security is paramount, but shouldn’t impair the effectiveness of customer master data management practice which extends beyond ensuring data privacy and unauthorized access. In the modern enterprise landscape, data is spread across a myriad of applications, each with its own unique metadata structure and terminologies. This poses a significant challenge in achieving a unified understanding of the same data across applications and systems.
Enter metadata interoperability. Metadata interoperability for customer master data revolves around creating an environment where metadata seamlessly interacts and flows across diverse applications and systems within the data ecosystem. This enables a holistic view of customer data, enhancing the quality and usability of that information across the organization.
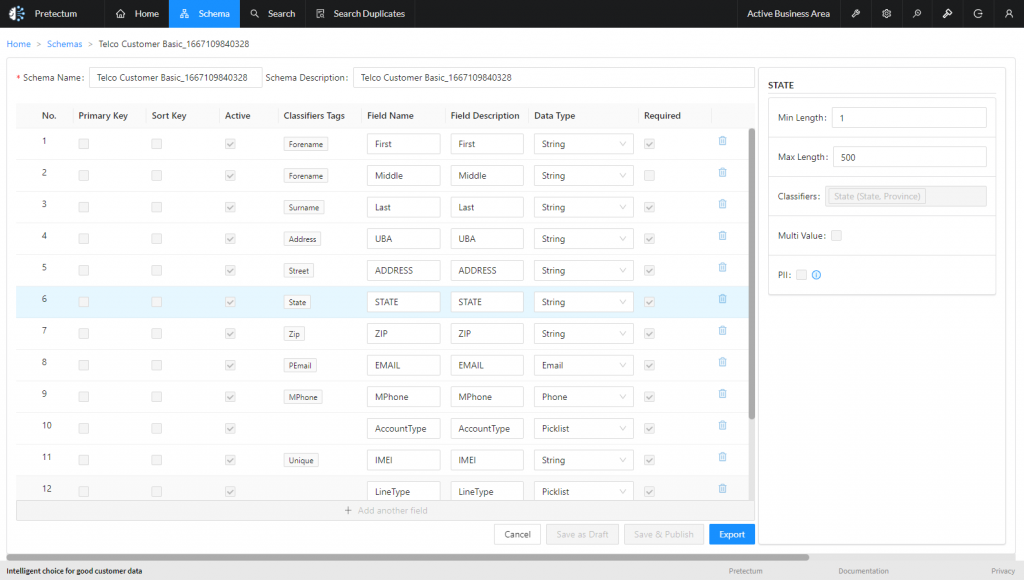
A robust metadata interoperability strategy calls for standardizing the data models, terminologies, and ontologies that will be leveraged to bridge the gap between the disparate systems. This fosters a shared understanding of data and accelerates decision-making processes, as employees become able to confidently navigate and comprehend customer data regardless of its source and labeling.
The evolution of expectations from Customer Master Data Management systems has benefited from the construction of transformative capabilities that have redefined data management paradigms. Centralized data security and visibility systems are emerging as a necessity to combat the challenges (and risks) posed by stovepipe applications. These systems streamline access controls, enhance compliance efforts, and optimize data governance.
CMDM’s ability to collaborate with external authorities is crucial for a cohesive and integrated approach to data security. By leveraging existing authorization and security rules, organizations can establish a consistent and robust security framework that transcends individual applications.
Moreover, the emphasis on metadata interoperability introduces a new dimension to CMDM’s role. Organizations can no longer afford to operate in silos; a unified understanding of data is pivotal for informed decision-making. Metadata interoperability bridges the gap between applications and systems, fostering a shared data understanding that enhances efficiency and productivity.
As enterprises grapple with an ever-expanding data landscape, the evolution of CMDM is poised to play a central role in shaping data security practices and promoting seamless data interoperability. By embracing these disruptive trends, organizations can navigate the complexities of modern data management with confidence, empowering them to unlock the true potential of their customer master data assets.