Master Data Management (MDM) and Customer MDM (CMDM) in particular, offers several advantages over Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, particularly in the context of data governance and quality.
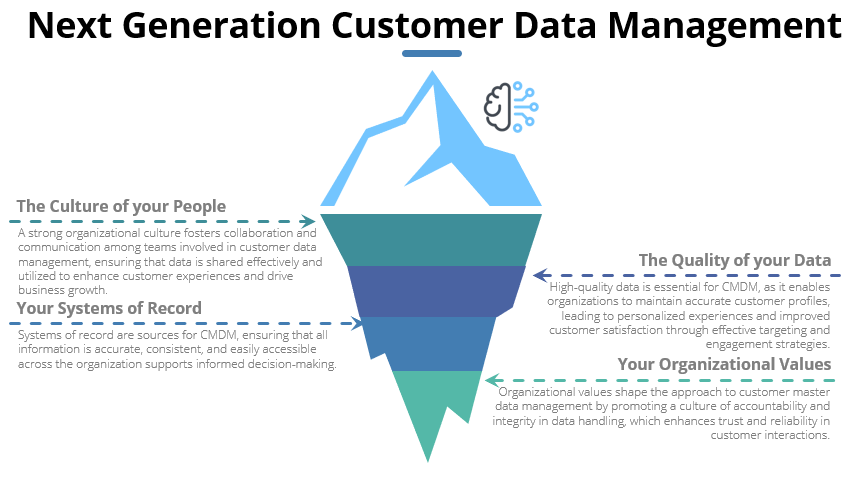
- Centralized Data Governance: CMDM provides a centralized repository for customer master data, to ensure consistency and accuracy of customer profiles across an organization. Centralization helps prevent data duplication and errors, which are common in CRM and ERP systems – CRM and ERP often operate as data and function silos.
- Incremental Implementation: CMDM can be implemented incrementally, this allows an organization to start with specific departments or data types, like service, support or sales. Such flexibility is particularly beneficial for organizations with budget constraints, as they can expand their use of CMDM and its capabilities over time without needing a full-scale deployment of the solution or technology from the outset. CRM and ERP are often very broad in capability and require a significant organizational commitment.
- Enhanced Data Quality: CMDM focuses on improving the quality of customer master data through processes such as data cleansing, standardization, and validation. This leads to more reliable data for decision-making compared to the often rudimentary customer data management capabilities found in ERP systems.
- Cross-Departmental Access: With CMDM, all permitted departments and users have access to either the same master data or a version of their data that is visible in a unified state, this fosters better internal and cross departmental collaboration and informed decision-making across the organization. In sharp contrast, ERP systems may limit customer data visibility to specific functions.
- Compliance and Risk Management: CMDM helps organizations comply with data-related regulations (privacy and data handling) by providing better control over data management practices. This capability is crucial for mitigating risks associated with data loss, data breaches and data inaccuracies.
- Improved Analytics and Insights: By ensuring high-quality customer master data, CMDM enhances the ability to perform accurate analytics and generate insights. This is particularly useful for initiatives that are non transactional, and where master data quality is paramount for effective analysis and decision making.
- Support for Diverse Data Sources: CMDM can integrate data from different source systems (including files, CRM and ERP), this provides a unified view of the customer master data across the organization. Integration is essential for companies that operate in multiple markets or have undergone mergers and acquisitions, or function in a distributed fashion, and where customer master data consistency is often a challenge.
While CRM and ERP systems are essential for managing customer relationships and operational processes, CMDM excels in establishing a strong foundation of customer master data quality and governance, which is critical for the success of any data-driven organization.

